As 5G reality edges ever-closer, the supporting technology will need to undergo a monumental shift for the underlying infrastructure to truly support and enable widespread connectivity.
The thing is, we’ve all become comfortably accustomed to the traditional data centre – and, more recently, the gargantuan power of all things cloud-based, including data storage. Until that is, we all developed a penchant for something more advanced: namely the IoT (Internet of Things) and, very soon, 5G.
The 5G conundrum
5G tech is receiving plenty of hype – and for good reason. The term has been rolling off the tongue for some years now, but the time is almost here for this high throughput cellular technology to hit the mainstream. When it does, it’ll be as pivotal to technology advancement as the evolution of the internet rollout to the public in the 1990s.
However, there’s one aspect of 5G technology that’s shaking up the role of the data centre in a way not seen for decades – and it all stems from the fact that the millimetre waves and microwaves it uses don’t travel very far. Hence traditional, centrally-located data centres won’t have the underlying infrastructure necessary for end-to-end 5G technology to work.
So what’s the answer?
It’s probably not what you think…
5G will rely on an edgier kind of data centre
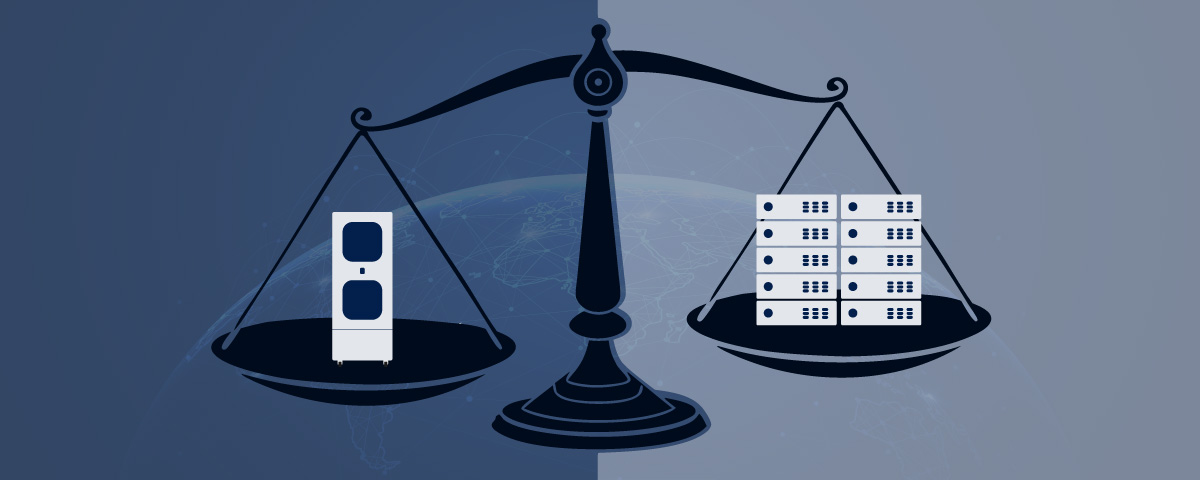
For almost three decades, the evolution of the data centre has been focused on enormous central locations housing ever-increasing amounts of data. But this won’t work for 5G. Instead, the whole system needs data storage and processing far closer to the action – a term known as ‘edge computing’. For 5G to work, the capacity and processing power needs to be closer to the end user, not squirrelled away in some gargantuan data storage centre thousands of kilometres away.
5G requires multiple small stations to serve a given area. This will service the relatively limited distance that 5G waves can travel – effectively allowing them to leapfrog from station to station. Data will be managed and processed not by traditional, large data centres, but smaller versions – the micro data centre.
Micro data centres might not be something that everyone is familiar with, but the technology has been being honed for well over a decade. When it comes to edge computing needs, nothing hits the spot better than a micro data centre. This advanced version of data storage and management is light-years away from the large, centralised versions of old. Multiple small 5G stations humming with the edge computing power of micro data centres is exactly what will power the 5G rollout.
Continuous data movement for 5G will be dependent on this advanced technology. And it’s already out there. The demand for data storage and processing at the edge is increasing year-on-year. By 2025 it’s estimated that 75% of enterprise-generated data will be outside that of the traditional data centre or the cloud.
Right now, we’re poised on the precipice of change (or should that be, the ‘edge’ of change). The role of the data centre is evolving – and it won’t be long before we all benefit from it.
Get in touch to find out more about our edge ready micro data centres.