Manufacturing in Australia is – at last – benefiting from a targeted government campaign to help revive it to the glory days of the 1960s. With financial backing and incentives, the industry is in the infancy of its growth stage. One vital aspect that’s set to play an enormous role in the re-emergence of the sector is that of Smart Manufacturing in combination with Edge computing.
Smart manufacturing: The data-centric rise of a neglected industry
Manufacturing used to account for over 30% of GDP during the 1960s. Today, that figure has fallen to a mere 5.6%. The key to advancing back towards those halcyon days is simple: productivity.
Edge computing is the silver bullet that presents the opportunity to increase output – something that savvy operators are already taking advantage of.
The concept of life on the Edge means bringing data capture and analysis closer to the place it occurs. Doing this brings about 5 distinct advantages – all of which are necessary to leap from a traditional to a smart manufacturing process that will provide the baseline to dramatically increase productivity.
The main advantages are as follows:
Data Analytic Management: We can’t go any further without mentioning the Internet of Things (IoT). These are, quite simply, connected devices that generate data – such as smart monitors embedded in a food production line to identify a contaminant. This data can then be acted on in real-time to prevent a catastrophic event, such as contaminated items entering the food chain. Such devices generate huge amounts of data. Having to send it vast distances to a data centre or to the cloud to be sifted requires enormous levels of storage, bandwidth and computing power. Edge computing, on the other hand, processes this data right where it occurs. It allows an instant reaction and frees up the strain on the wider network.
Reduced latency: Transferring data to a main centre or the cloud takes time. While this might only be measured in milliseconds, this so-called ‘latency’ represents valuable time where a necessary action is delayed. The impact of this can be tremendous, especially in time-critical manufacturing. Damage to equipment, inferior products or even injury/risk to human life is increased if data isn’t acted upon in real-time. No interconnected system can work to its true potential without instant data analysis.
Increased interoperability: No manufacturing process occurs without systems communicating with each other. The challenge today is that various devices are often not compatible with each other. Bringing Edge computing into the mix removes a lot of such issues, as the data doesn’t all have to be sent back to a single source for analysis. The upshot of this is that it allows more systems to work seamlessly with each other, without having to alter existing smart devices or manufacturing processes.
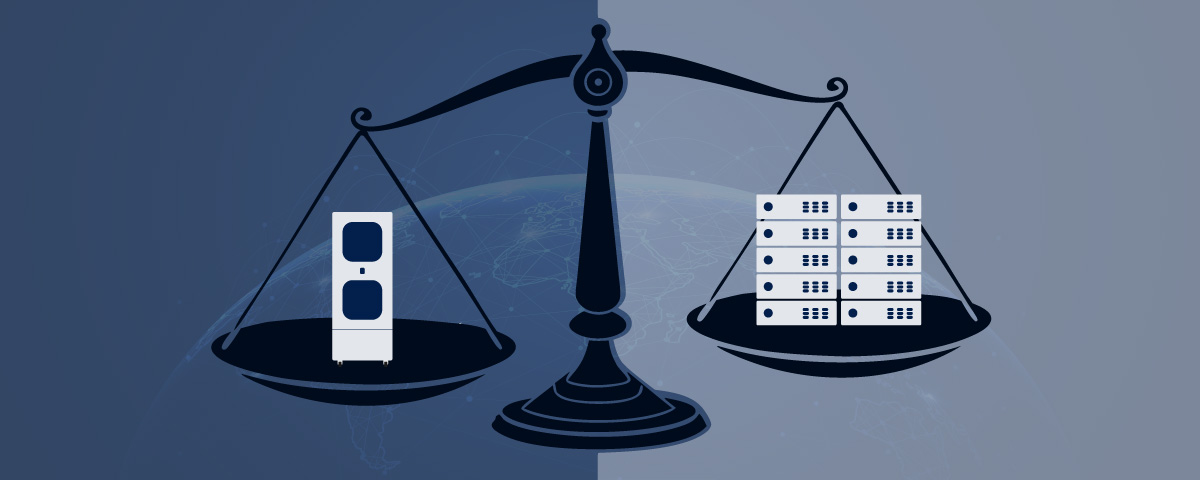
Cheaper storage: Data analysis and storage costs money. Whether this involves constructing and running a local data storage room or sending it to the cloud, the costs will rise exponentially as data generation increases. Edge computing allows data to be sifted at source with only relevant information being passed along the line. Add in the advantages of Micro Data Centres (MDCs) and necessary data can be stored locally, meaning the whole system can easily be compartmentalised and segmented.
Better security: Cybersecurity is a major concern, with hacking situations regularly making news headlines. Every smart device within a system presents a potential portal for infiltration, with traditional data storage and network solutions increasing that vulnerability. Storage at the edge considerably reduces that risk. By spreading storage throughout a facility means there’s no central point of entry. This means a single attack can’t, therefore, debilitate the complete system.
Bringing storage to the Edge necessitates a simple solution that’s easy to implement, maintain, and – very importantly – upscale when required. Micro Data Centres neatly fit this niche and are being embraced by businesses of all sizes, thanks to their affordability and ease of use. Have a look at some success stories from our manufacturing clients.
Find out more about our products and their benefits or get in touch to find out how we can help your business.