Climate change and sustainability have become political factors that play a growing role in business management. There is more and more pressure for companies to limit their greenhouse gas emissions and take action to become more environmentally friendly.
Carbon emissions from data centres and server rooms are a growing global concern with the rapidly increased demand for data processing and storage. But what is driving the growth of data?
Why so much data?
Remember when your laptop came with 40GB of data and you thought that was a lot? Now even the most basic phone comes with a similar amount of data storage … and we run out of space so quickly we end up storing most of our photos and videos on the cloud! Think about how much data you generate every day: google searches, social media, YouTube videos, GPS tracking, contactless debit card, browsing the internet, streaming songs or movies … and this just in your personal life!
It’s easy to see how the world’s data has grown exponentially since the invention of the internet and that it will keep growing fast as technology keeps advancing. And of course the more data we use, the more data centres we need.
The realities of data centre carbon emissions
Currently the global carbon footprint for data centres accounts for more than 2% of global carbon emissions (the equivalent of the world’s entire airline industry), with the number expected to rise to 3.2% in 2025. By 2040, data storage is predicted to account for 14% of the world’s carbon emissions.
Data centres require a significant amount of energy to power and cool the servers that store and process vast amounts of digital information. This energy consumption is primarily driven by the need to keep the servers running at all times and to maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels to prevent damage to the equipment. Cooling the IT equipment in a data centre is biggest power guzzler, accounting for more than 40% of total energy consumption.
So how do you reduce your company’s carbon emissions?
 You many not be able to use less data, but if you oversee your company’s IT department, you can take measures to reduce the energy consumption of your data centre; this will have a big impact on your company’s overall carbon emissions (and power bills!).
You many not be able to use less data, but if you oversee your company’s IT department, you can take measures to reduce the energy consumption of your data centre; this will have a big impact on your company’s overall carbon emissions (and power bills!).
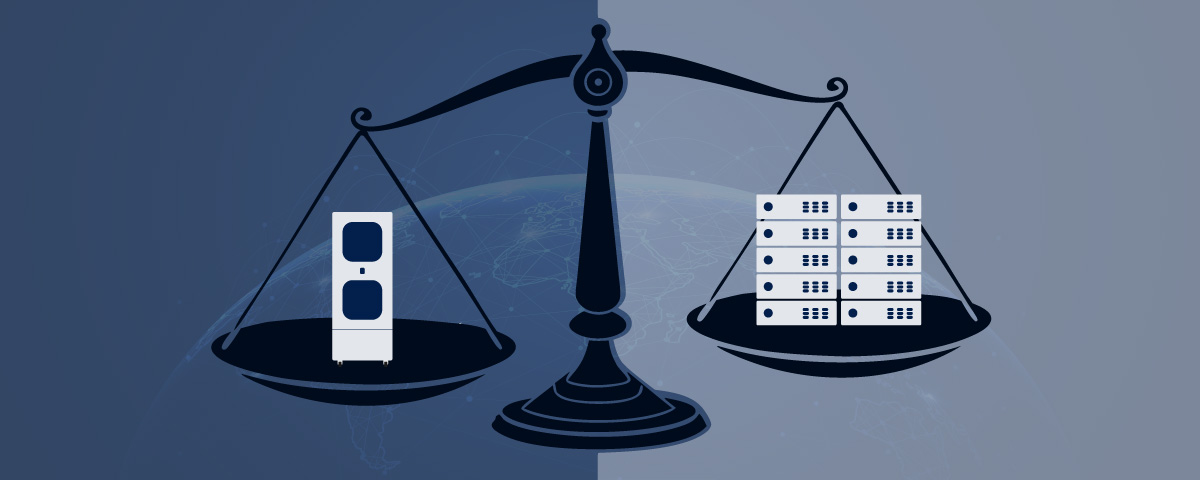
A simple and effective way to reduce your company’s carbon footprint (and improve your NABERS rating) is by upgrading to a micro data centre. This all-in-one solution is typically more energy efficient than a traditional on-premise server room and data centres typically by 20% or more, reducing the cooled area from a whole room or floor to an area the size of an average refrigerator. Storing and processing data in a micro data centre at the edge is also typically more environmentally friendly than sending large amounts of data to the cloud.
Micro data centres offer several benefits and options in reducing carbon emissions:
- Energy Efficiency: Micro data centres are designed to be highly efficient and optimise energy consumption. They use energy-saving technologies such as virtualisation, efficient cooling systems, and efficient power supplies, which reduces the overall energy consumption of the data centre.
- Renewable Energy Ready Options: Companies can power their micro data centres with renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, or hydro power, which reduces their reliance on fossil fuels and lowers their carbon footprint.
- Localised Computing: Micro data centres can be placed closer to the end-users, which reduces the need for data to travel long distances over the internet, reducing the carbon emissions associated with data transmission.
- Reduced Infrastructure: Micro data centres require less infrastructure than traditional data centres, which reduces the carbon emissions associated with construction and maintenance.
- Waste Reduction: Micro data centres generate less waste and require fewer resources to operate, reducing the environmental impact of the data centre.
With micro data centres, companies can significantly reduce their carbon emissions, making it a sustainable and environmentally responsible choice for managing data.
A greener micro data centre
But of course not all micro data centres offer the same energy saving measures.
At Zella DC we have developed a range of micro data centres designed to be user friendly, efficient, secure and compact. The Zella Pro is at the core of all our products and has been designed with sustainability in mind:
- Compact – reduce the cooled area from an entire room / floor to an area the size of a refrigerator
- Smart technology – match your cooling and energy efficiencies with your IT load at all times
- Highly efficient – with a PUE as low as 1.2
- Precision cooling system to maintain constant temperature and humidity
- Fully sealed with thermal insulation to maximise cooling efficiency
- DC powered option makes it easier to connect to renewables
And to top it all off, such a highly efficient micro data centre will also reduce your power bills and maintenance expenses.
Get in touch to find out more or head over to our products page to find out more.